- Visibility 122 Views
- Downloads 43 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijmpo.2024.024
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Diagnostic value of umbilical cord blood culture compared to sepsis screening in high-risk neonates
Introduction
Sepsis is a potentially fatal illness that develops when the body injures its own tissues and organs as a reaction to an infection.[1] Neonatal septicaemia is defined as a clinical illness with systemic signs and symptoms resulting from a widespread bacterial infection with a positive blood culture within the first four weeks of life.[2]
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition in neonates, particularly in developing countries, where neonatal sepsis contributes significantly to early mortality. Early-onset neonatal sepsis (EOS), occurring within 72 hours of birth, has high fatality rates, making prompt diagnosis essential. [3]
Current diagnostic standards often rely on peripheral venous blood culture and sepsis screening, but challenges like sample volume inaccuracy and multiple puncture attempts can limit effectiveness. Umbilical cord blood collection, while less commonly used, offers advantages such as ease, minimal discomfort, and sufficient sample volume. [4]
This study aimed to compare the diagnostic utility of umbilical cord blood culture (UCBC) with standard sepsis screening methods in high-risk neonates to assess its potential for faster, reliable EOS detection. The study variables included gestational age, mode of delivery, birth weight, and gender, as these are known to influence the likelihood of sepsis in neonates. Gestational age was categorized into ≤34 weeks, 34–36 weeks, and ≥37 weeks. The mode of delivery was classified as vaginal delivery or cesarean section (LSCS), while birth weight was categorized into low birth weight (<2500g), normal birth weight (2500–4000g), and high birth weight (>4000g). The gender of the neonates was also recorded, as studies have shown a slight gender-based difference in sepsis incidence. These variables were evaluated in relation to the diagnostic outcomes of UCBC and sepsis screening to understand their role in EOS detection.
Materials and Methods
Study setting and population
This study was conducted in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, Department of Paediatrics, Karnataka Institute of Medical Sciences (KIMS), Hubballi, Karnataka, including all newborns at KIMS at high risk for early onset neonatal sepsis.
Study design
Prospective analytical study conducted from June 2022 to February 2024 that is twenty months
Sample size
62 newborns with high-risk factors for early onset sepsis, estimated based on a UCBC sensitivity of 75% from prior studies.
Inclusion criteria
Newborns with two or more risk factors for sepsis, including prolonged rupture of membranes for more than 18 hours, prolonged labor for more than 24 hours, maternal febrile illness within 2 weeks of delivery, low birth weight less than 2.5 kg, prematurity less than 37 weeks, meconium-stained or foul-smelling liquor, and frequent per vaginal exams (more than 3 times) during labor.
Exclusion criteria
Neonates with life-threatening congenital anomalies.
Ethics and consent
Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee, KIMS Hubballi. Written informed consent was obtained from parents or guardians.
Data collection and blood sampling
Umbilical cord blood (UCBC) was collected immediately after delivery, and peripheral venous blood was collected within 24 hours for sepsis screening (Total Leukocyte Count, Absolute Neutrophil Count, IT Ratio, C-reactive protein, Micro ESR). For UCBC, 1 mL blood was drawn aseptically from the placental end of the cord after cleaning with 70% isopropyl alcohol and povidone iodine. For peripheral venous blood, 1 mL was collected using similar aseptic procedures. Both samples were injected into BACT/ALERT bottles for bacterial culture.
Results
In our study titled “Diagnostic Value of Umbilical Cord Blood Culture Compared to Sepsis Screening in High-Risk Neonates,” conducted over twenty months from June 2022 to February 2024, 62 neonates who met the inclusion criteria were enrolled after obtaining informed parental consent and clearance from the institutional research and ethical committees.
Demographic data
Mode of Delivery: The majority of neonates, 37 (59.7%), were delivered via normal vaginal delivery, while 25 (40.3%) were delivered by lower-segment cesarean section (LSCS).
Gestational age
Most neonates, 23 (37.1%), were delivered at or before 34 weeks of gestation. An equal proportion of neonates, 20 (32.3%) each, were delivered between 34–36 weeks and at 37 weeks or later.
Birth weight
The largest group of neonates, 33 (53.2%), had birth weights between 1,500–2,500 grams. This was followed by 15 (24.2%) neonates weighing more than 2,500 grams and 14 (22.6%) weighing less than 1,500 grams.
Gender
Male neonates constituted a majority, with 34 (54.8%), while females accounted for 28 (45.2%).
UCBC and sepsis screening results
Out of the 62 neonates, 12 (19.4%) had a positive umbilical cord blood culture (UCBC), while 50 (80.6%) had a negative UCBC. Sepsis screening results showed that 19 (30.6%) neonates had positive sepsis screening, while 43 (69.4%) had negative results ([Table 1]).
Diagnostic performance of UCBC
When compared to sepsis screening, the sensitivity of UCBC was found to be 57.9%, and specificity was 97.7%. The positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were 91.7% and 84.0%, respectively ([Table 2]).
Sepsis screening parameters
Sepsis screening included total leucocyte count (TLC), absolute neutrophil count (ANC), immature-to-total neutrophil ratio (I/T ratio), C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and micro ESR ([Table 3]). The mean values were as follows:
TLC: 10,415.81 ± 6,293.74
ANC: 5,635.48 ± 5,388.75
I/T Ratio: 0.15 ± 0.07
CRP: 1.40 ± 2.34
Micro ESR: 5 ± 2 mm/hr
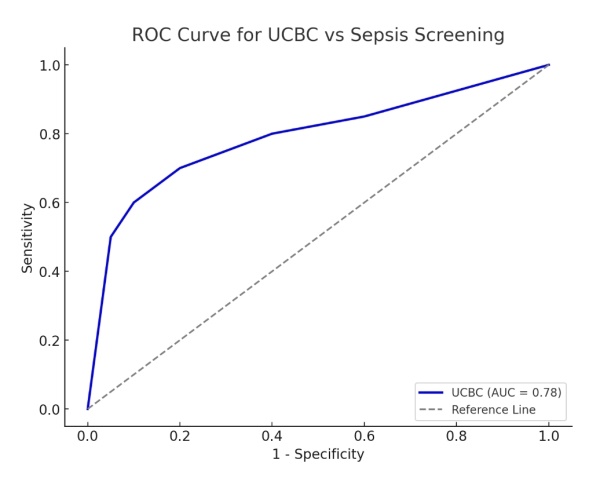
ROC curve analysis
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for UCBC demonstrated an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.78, indicating moderate diagnostic accuracy. This suggests that UCBC achieves a reasonable balance between sensitivity and specificity when sepsis screening is used as the reference standard ([Figure 1]).
|
Test/Variable |
Frequency |
Proportion (%) |
|
UCBC |
|
|
|
Positive |
12 |
19.4% |
|
Negative |
50 |
80.6% |
|
Sepsis screening |
|
|
|
Positive |
19 |
30.6% |
|
Negative |
43 |
69.4% |
|
UCBC |
Sepsis screening |
|||
|
Positive |
Negative |
|||
|
Frequency |
% |
Frequency |
% |
|
|
Positive |
11 |
57.9 |
1 |
2.3 |
|
Negative |
8 |
42.1 |
42 |
97.7 |
|
|
19 |
100.0 |
43 |
100.0 |
|
Diagnostic Accuracy Metrics of UCBC |
||||
|
Sensitivity |
57.9% |
|
||
|
Specificity |
97.7% |
|||
|
Positive predictive value |
91.7% |
|||
|
Negative predictive value |
84% |
|
Sepsis screening |
TLC |
ANC cells /mm3 |
I/T ratio |
CRP |
MICRO ESR mm/hr |
|
Mean |
10415.81 |
5635.48 |
0.15 |
1.40 |
5 |
|
Std. Deviation |
6293.74 |
5388.75 |
0.073 |
2.348 |
2 |
Discussion
The present study was conducted in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of the Department of Paediatrics at Karnataka Institute of Medical Sciences (KIMS), Hubballi, Karnataka, in collaboration with the Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. A total of 62 newborns who met our inclusion criteria and exhibited high-risk factors for early-onset neonatal sepsis (EONS) were recruited. Umbilical cord blood (UCB) was collected immediately after delivery, along with peripheral vein blood and samples for sepsis screening, within 24 hours of birth for neonates with two or more sepsis risk factors. The typical presentation of EONS is a multisystemic, fulminant illness resulting from vertical transmission from the mother, characterized by progressive symptoms with focal infection as a hallmark. Compared to late-onset sepsis, EONS carries a higher case fatality rate. [5]
Gender: Among the neonates at high risk for EONS in our study, the majority were males (54.8%), followed by females (45.2%). These findings align with previous studies conducted by Aundhakar et al., [5] and Alam MS et al.,[6] which also reported a male predominance. One theory posits that males are more susceptible to sepsis due to immunoglobulin synthesis factors located primarily on the X chromosome. [7] However, in contrast, a study by Kalathia MB et al., [8] reported a higher incidence of sepsis in females.
Gestational Age: In the current study, 37.1% of neonates were delivered at or before 34 weeks of gestation, with a mean gestational age of 34.7 ± 3.5 weeks. These results were consistent with studies conducted by Meena et al., [9] Aundhakar CD et al., [5] and Alam MS et al., [6] which reported similar mean gestational ages of 36.6 ± 0.7 weeks, 36.6 ± 0.7 weeks, and 33.96 ± 1.82 weeks, respectively.
Mode of Delivery: Vaginal delivery accounted for the majority of cases (59.7%) in this study, followed by lower-segment cesarean section (LSCS) in 40.3% of cases. These results were consistent with findings by Ojha M et al., [10] who reported 48% vaginal deliveries, 46% LSCS, and 6% instrumental vaginal deliveries. However, contrasting results were reported by Alam MS et al., [11] and Aundhakar CD et al., [5] where LSCS predominated.
Birth Weight: A significant proportion (75.8%) of neonates in this study were categorized as having low birth weight (< 2,500 grams), while 24.2% weighed more than 2,500 grams. Most of the neonates (51.6%) weighed between 1.5 and 2.5 kilograms. Similar findings were reported by Ojha et al., [10] and Aundhakar CD et al., [5] who observed mean birth weights of 1,956 ± 667 grams and 2,250 ± 685 grams, respectively. Alam MS et al., [6] reported a mean birth weight of 1,900 ± 483.6 grams, with a range of 1,200–3,000 grams.
Sepsis Screening and UCBC Results: In this study, 30.6% of neonates had positive sepsis screening, while 19.4% showed UCBC positivity. These findings were consistent with Aundhakar CD et al., [5] who reported 32.0% sepsis screen positivity, 17.3% UCBC positivity, and 5.3% PVBC positivity. However, unlike our findings, their study found that samples positive by sepsis screening were also positive in both UCBC and PVBC cultures.
Herson et al., [12] observed a 20.0% (7/35) UCBC positivity rate among high-risk newborns, while Fos et al., [13] reported 43.3% (13/30) UCBC positivity in their cohort. Kalathia MB et al., [8] noted 17.8% PVBC and 24.4% UCBC positivity. All neonates with positive culture results in these studies had clinical sepsis and positive sepsis screens.
Challenges in Sepsis Diagnosis: Collecting adequate blood for PVBC and sepsis screening is a significant challenge. Antibiotic administration before blood collection often results in no growth in PVBC. Additionally, venipuncture in neonates demands high technical skill and considerable time. [5]
Historical Context of UCBC Use: Pryles et al., (1963) [14] highlighted the impact of chorioamniotic infection on newborns using UCBC on 150 patients. Albers and Tyler (1966) [15] explored umbilical cultures for diagnosing neonatal sepsis. Polin et al., (1981) [16] reported UCBC’s utility in diagnosing neonatal sepsis with 200 samples. Herson et al., [12] demonstrated its usefulness for high-risk neonates using blood from umbilical veins. Hansen et al., (2005) [17] confirmed UCBC’s safety for complete blood count analysis and sepsis evaluations in asymptomatic term infants. Costakos et al., (2006) [18] demonstrated that UCBC collection is dependable and less painful, replacing traditional blood culture methods as part of universal screening for EONS based on maternal risk factors. Fos et al., (2010) [13] concluded that UCBC is a more practical and straightforward diagnostic method for neonatal sepsis.
Conclusion
UCBC is an easy-to-perform, painless, and early test to diagnose EOS. It has a high PPV of 91.7%, making it a useful tool. However, a relatively low sensitivity of 57.9% suggests the need for its use in conjunction with additional rapid sepsis screening tools to improve the accuracy of EOS diagnosis.
Instead of pricking the newborns in order to collect blood, UCBC may be a more comfortable, kind, and painless method.
Ethical Committee Approval
Study was initiated after obtaining approval from the Institutional Ethics Committee of KIMS, Hubballi. (Reg no.: ECR/486/Inst/KA/2013/RR-16]
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- . World Health organization. Sepsis. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- HR Hassan, JR Gohil, R Desai, RR Mehta, VP Chaudhary. Correlation of Blood Culture Results with the Sepsis Score and Sepsis Screen in the Diagnosis of Early-onset Neonatal Septicemia. J Clin Neonatol 2016. [Google Scholar]
- C Fleischmann, F Reichert, A Cassini, R Horner, T Harder, R Markwart. Global incidence and mortality of neonatal sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child 2021. [Google Scholar]
- R Milton, D Gillespie, C Dyer, K Taiyari, M J Carvalho, K Thomson. Neonatal sepsis and mortality in low-income and middle-income countries from a facility-based birth cohort: an international multisite prospective observational study. Lancet Glob Health 2022. [Google Scholar]
- C D Aundhakar, H Tatiya, G Karande, S Akhila, K Madhura. Study of umbilical cord blood culture in diagnosis of early-onset sepsis among newborns with highrisk factors. Int J Med Health Res 2018. [Google Scholar]
- MS Alam, MA Mannan, SK Dey, AZM Raihanur Rahman, M Shahidullah. Umbilical Cord Blood for the Screening of Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis among Those at Risk of Infection. Sch J App Med Sci 2009. [Google Scholar]
- M Varshney, S Misra, A Bhambri. Prospective study of umbilical cord blood culture for early diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis. Int J Adv Integ Med Sci 2021. [Google Scholar]
- MB Kalathia, PA Shingala, PN Parmar, YN Parikh, IM Kalathia. Study of umbilical cord blood culture in diagnosis of early-onset sepsis among newborns with high-risk factors. J Clin Neonatol 2013. [Google Scholar]
- R Meena, KK Meena, V Athwani, S Gothwal, GS Bairwa, S Sitaraman. Umbilical Cord Blood Culture in Diagnosis of Early Onset Neonatal Sepsis. Indian J Pediatr 2020. [Google Scholar]
- M Ojha, A Pradhan, S Dutta, A Jaiswal. Use of umbilical cord blood culture in the diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis among high risk mothers. Asian J Med Sci 2021. [Google Scholar]
- P Jain, M Gosai. Prospective comparative study of umbilical cord blood culture versus peripheral venous blood culture in diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis in neonatal intensive care unit of tertiary care hospital in Bhavnagar. J Neonatal Bio 2021. [Google Scholar]
- VC Herson, C Block, JC Mclaughlin, J Tetreault, LI Eisenfeld, PJ Krause. Placental blood sampling: an aid to the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. J Perinatol 1998. [Google Scholar]
- NI Fos, RV Gomis, CV Gomis, J Rubio, P Justich, JC Valera. Blood culture from the umbilical vein in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Internet J Pediatr Neonatol 2010. [Google Scholar]
- CV Pryles, LN Steg, S Nair, SS Gellis, B Tenney. A controlled study of the influence on the newborn of prolonged premature rupture of the amniotic membranes and/or infection in the mother. Pediatrics 1963. [Google Scholar]
- CW Tyler, WH Albers. Obstetric factors related to bacteremia in the newborn infant. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1966. [Google Scholar]
- JI Polin, I Knox, S Baumgart, E Campman, MT Mennuti, RA Polin. Use of umbilical cord blood culture for detection of neonatal bacteremia. Obstet Gynecol 1981. [Google Scholar]
- A Hansen, P Forbes, R Buck. Potential substitution of cord blood for infant blood in the neonatal sepsis evaluation. Biol Neonate 2005. [Google Scholar]
- DT Costakos, J Walden, MT Rinzel, L Dahlen. Painless blood testing to prevent neonatal sepsis. WMJ 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Materials and Methods
- Study setting and population
- Study design
- Sample size
- Inclusion criteria
- Exclusion criteria
- Ethics and consent
- Data collection and blood sampling
- Results
- Demographic data
- Gestational age
- Birth weight
- Gender
- UCBC and sepsis screening results
- Diagnostic performance of UCBC
- Sepsis screening parameters
- ROC curve analysis
- Discussion
- Conclusion
- Ethical Committee Approval
- Conflict of Interest
- Source of Funding
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Gudagunti MM, Desai RH. Diagnostic value of umbilical cord blood culture compared to sepsis screening in high-risk neonates [Internet]. IP Int J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2025 [cited 2025 Sep 04];10(4):92-96. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijmpo.2024.024
APA
Gudagunti, M. M., Desai, R. H. (2025). Diagnostic value of umbilical cord blood culture compared to sepsis screening in high-risk neonates. IP Int J Med Paediatr Oncol, 10(4), 92-96. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijmpo.2024.024
MLA
Gudagunti, Monica M, Desai, Raghavendra H. "Diagnostic value of umbilical cord blood culture compared to sepsis screening in high-risk neonates." IP Int J Med Paediatr Oncol, vol. 10, no. 4, 2025, pp. 92-96. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijmpo.2024.024
Chicago
Gudagunti, M. M., Desai, R. H.. "Diagnostic value of umbilical cord blood culture compared to sepsis screening in high-risk neonates." IP Int J Med Paediatr Oncol 10, no. 4 (2025): 92-96. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijmpo.2024.024
